Accounting Basics: Assets, Liabilities, Equity, Revenue, and Expenses

Retained earnings are the net earnings a company either reinvests in the business or uses to pay off debt. The remaining amount is distributed to shareholders in the form of dividends. A liability is any money that a company owes https://x.com/BooksTimeInc to outside parties, from bills it has to pay to suppliers to interest on bonds issued to creditors to rent, utilities and salaries. Current liabilities are due within one year and are listed in order of their due date. Long-term liabilities, on the other hand, are due at any point after one year. Everything listed is an item that the company has control over and can use to run the business.

Financial Accounting

The first is money, which is contributed to the business in the form of an investment in exchange https://www.bookstime.com/ for some degree of ownership (typically represented by shares). The second is earnings that the company generates over time and retains. A balance sheet represents a company’s financial position for one day at its fiscal year end, for example, the last day of its accounting period, which can differ from our more familiar calendar year.
- Explore our online finance and accounting courses, which can teach you the key financial concepts you need to understand business performance and potential.
- These accounts have different names depending on the company structure, so I list the different account names in the chart below.
- The remainder is the shareholders’ equity, which would be returned to them.
- For example, if a large company maintains its own fire station on its grounds, the building and the equipment are considered assets by this definition.
- Everything listed there is an item that the company has control over and can use to run the business.
- Again, separate these according to current and noncurrent liabilities.
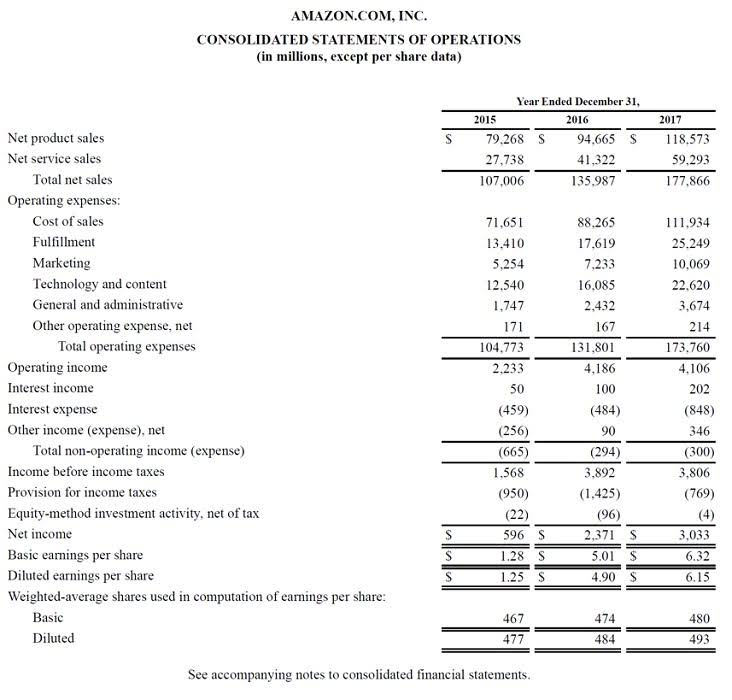
- The image below is an example of a comparative balance sheet of Apple, Inc.
Accounting equation
This section will discuss the relationship between equity and shareholder relations, focusing on common and preferred stock and retained earnings. The accounting equation states that a company’s total assets are equal to the sum of its liabilities and its shareholders’ equity. Liabilities are obligations that the company owes to external parties, such as loans, accounts payable, and accrued expenses. Equity represents the residual claim on assets after satisfying liabilities. A company can pay for something by either taking out debt (i.e. liabilities) or paying for it with money they own (i.e. equity). Therefore, the equation reflects the principle that all of a company’s resources (assets) can be paid in one of those two ways.
Components of the Balance Sheet

Income is money the business earns from selling a product or service, or from interest and dividends on marketable securities. Other names for income are revenue, gross income, turnover, and the “top line.” Examples of liability accounts that display on the Balance Sheet include Accounts Payable, Sales Tax Payable, Payroll Liabilities, and Notes Payable. Assets can be defined as objects or entities, both tangible and intangible, that the company owns that have economic value to the business. Using accounting software can help ensure that each journal entry you post keeps the formula in balance. If you use a bookkeeper or an accountant, they will also keep an eye on this process.
○ Types of Equity Accounts ○
- Assets, liabilities, and equity are the three primary components of a balance sheet.
- Accounting software can easily compile these statements and track the metrics they produce.
- Although the balance sheet is an invaluable piece of information for investors and analysts, there are some drawbacks.
- In this article, we help you to become more familiar with the overall structure of the balance sheet.
- A balance sheet reports your firm’s assets, liabilities, and equity as of a specific date.
- No, all of our programs are 100 percent online, and available to participants regardless of their location.
Shareholders’ equity ultimately indicates the financing provided by the company’s owners and the earnings generated from its operations. Think of retained earnings as savings, since it represents the total profits that have been saved and put aside (or “retained”) for future use. When an investment is publicly traded, the market value of equity is readily available by looking at the company’s share price and its market capitalization.
- Every accounting entry has an opposite corresponding entry in a different account.
- Because of this, managers have some ability to game the numbers to look more favorable.
- That part of the accounting system which contains the balance sheet and income statement accounts used for recording transactions.
- The common stock and preferred stock accounts are calculated by multiplying the par value by the number of shares issued.
- Common examples of assets found on a balance sheet include accounts receivable, cash, buildings, and inventory.
As a core concept in modern accounting, this provides the basis for keeping a company’s books balanced assets = liabilities + equity across a given accounting cycle. Private equity is often sold to funds and investors that specialize in direct investments in private companies or that engage in leveraged buyouts (LBOs) of public companies. In an LBO transaction, a company receives a loan from a private equity firm to fund the acquisition of a division of another company. Cash flows or the assets of the company being acquired usually secure the loan. Mezzanine debt is a private loan, usually provided by a commercial bank or a mezzanine venture capital firm.

As a result of the transaction, an asset in the form of merchandise increases, leading to an increase in the total assets. At this point, let’s consider another example and see how various transactions affect the amounts of the elements in the accounting equation. Assets, liabilities, equity and the accounting equation are the linchpin of your accounting system.


